It is taken with the side of the patients chest compressed against the cassette. Chest axial CT images at the level of the pulmonary arteries in mediastinal windows.
On A Posteroanterior Chest X Ray The Right Hemithorax Is Very Dark Or Download Scientific Diagram
Axial cadaver radiograph of the sectioned chest at the level of the pulmonary arteries.

. AP projection left lateral decubitus would best demonstrate pneumothorax. The typical chest x-ray will be done with a detector cassette under the patient. Indicated where Chest XRay cannot distinguish bleb in COPD from Pneumothorax.
The routine examination of the ribs when the patients condition will permit must include an erect PA radiograph of the chest and each oblique projection of the affected side. Tips to help to find pneumothoraces include. In those with Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax due to blebs contralateral blebs are seen.
To view the right lung and heart the patients right side is placed against the cassette. Therapeutic chest drainage of a pneumothorax PNO is usually performed through the safe triangle just under the lateral border of the pectoralis muscle 1 2. The radiologic findings of pneumomediastinum are pivotal.
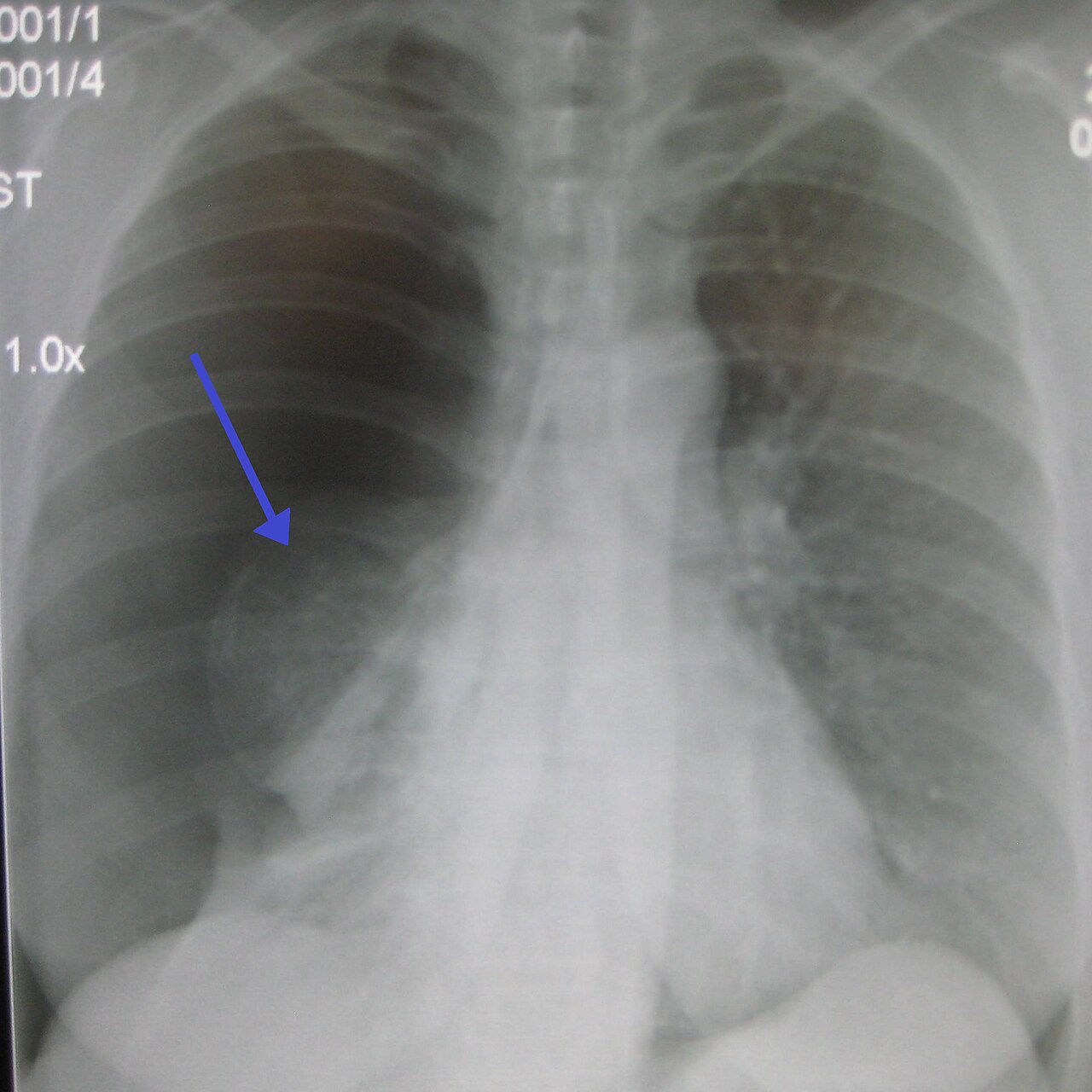
A normal lateral examination of the chest X-ray is shown to exemplify the positioning of the cardiac chambers showing the right ventricleRV right ventricular outflow tract RVOT and main pulmonary artery MPA anteriorly the left ventricle LV left atrium LA posteriorly with the SVC posterior to the ascending aorta Ao and the inferior. Air may outline the tissue. A patient comes to Radiology with a possible right pneumothorax.
No lateral view is done. This patients pneumothorax resolved spontaneously. Patient comes into radiology with a possible right pneumothorax.
The apex of the partially collapsed lung reaches the sixth posterior rib. Left apical pneumothorax is confirmed best seen on the expiratory view. A pneumothorax is seen as a region of lucency dark around the edge of the lung.
The patients arms are raised with the forearms resting on the head. This is difficult to see because the lung itself is black too. Small pneumothoraces tend to go to the lung apex and can be relatively easy to see on an upright chest x-ray.
An erect chest radiograph has a sensitivity as high as 92 for detection of a pneumothorax whilst a supine projection may only detect 50 6. Instead the pneumothorax may be demonstrated by looking for the following signs. Which chest projection would be ideal in demonstrating this condition.
The technologist used the following factors for the radiograph. Chest axial MR image at the level of the pulmonary arteries. Successful drainage of a PNO results in full re-expansion of the lung confirmed by chest ultrasound or less reliably by plain chest radiograph CXR 3 - 8.
The indications for the erect frontal examination of the chest include primarily the detection of possible pneumothorax pulmonary contusion or pleural effusion. They are more easily seen on erect chest x-rays as the free air typically rises up to the apex above the lung making it more visible. Indication Undertaken to demonstrate small pleural effusions or for the investigation of pneumothorax and air trapping due to inhaled foreign bodies.
Now let us think about a patient lying in bed supine. The management of pneumothoraces detected on CT but not on supine chest radiographs remains controversial especially in those undergoing positive pressure ventilation PPV who are. If effusion and pneumothoraxhydropneumothoraxare present an airfluid level is seen on the lateral decubitus projection.
The right lateral chest position is used to show right sided pulmonary lesions. If a pneumothorax is present and the examination is being made to investigate the air-outlined pleura the x-ray beam should be centered on the elevated rather than the recumbent side of the patient. A 72 inch SID an upright bucky a full inspiration exposure 75 kv and 600 ma and a.
The left lateral chest position is used to show the heart the aorta and left-sided pulmonary lesions. In the supine patient pneumothoraxes are best seen at the lung bases and adjacent to the heart Skin folds companion shadows the scapula and previous lung surgery or chest drain placement may all mimic pneumothoraxes. Flex arms and rest back of hands low on hips below level of costophrenic angles rotates scapula laterally Depress shoulders rotate them forward to position it below lung apices.
See Lung Ultrasound for Pneumothorax Sliding Lung Sign Test Sensitivity 94 and Test Specificity 100 for Pneumothorax. In the posteroanterior projection Fig 1 the mediastinal pleura isdisplaced laterally and is best seen on the left parallel to the heart border. The lateral radiograph is obtained to complement the PA radiograph.
A radiograph of a PA and left lateral projection of the chest reveals that the mediastinum of the chest is underpenetrated. Which of the following chest projections will best demonstrate the maximum area of the right lung. AP anteriorposterior AUC area under the receiver operating characteristic curve PA posterioranterior.
It is chiefly used in the pediatric population. Receiver operating characteristic curves for pneumothorax detection stratified by A pneumothorax size B presence of a chest tube and C projection of the chest radiograph. 2 case question available Case Discussion Pneumothorax is an uncommon complication of permanent pacemaker insertion.
In the posteroanterior projection Fig 1 the mediastinal pleura is displaced laterally and is best seen on the left parallel to the heart border. The lateral projections are employed extensively to show interlobar fissures differentiate the lobes i to localized pulmonary lesions. A lateral projection Fig 2 may double the detection rate by demonstrating retrosternalair or highlighting the thoracic aorta and knob with vertical translucent streaks.
Relative lucency of the involved hemithorax. She is unable to stand. Chest X-ray showing a pneumothorax on the right left in the image where the absence of lung markings indicates that there is free air inside the chest Chest X-ray showing the features of pneumothorax on the left side of the person right in image.
Gold standard in Pneumothorax. A radiologist wants an oblique projection that will demonstrate the maximum area of the right lung. AP oblique projection RPO position.
Stand straight weight equally distributed. The lateral decubitus view of the chest is a specialized projection that is now rarely used due to the ubiquity of CT. Approximate axial anatomic level through the pulmonary arteries for BD.

How To Identify Pneumothorax On A Chest X Ray Youtube
0 Comments