Dark-field microscopy produces high-contrast images of samples such as blood cells bacteria algae and marine organisms that are often transparent and provide little to no light absorption contrast. The microbes to be observed must be killed fixed and.
What Is The Principle Of Dark Field Microscopy Quora
The microbes are seen as dark objects.

. Fixation and stained preparation of specimens. The first is based on blocking the light rays that reach the condenser directly through the use of. To maximize the scattered light-gathering power of.
Dark-field microscopy depends on which characteristic of lightChoose one. In electron microscopy techniques the light source is the high accelerating electrons only. The specimen appears lit up agains a dark background.
4Bb while a bacterium without Au NPs was observed as an ambiguous rod Fig. Whereas bright field BF lighting is a more common application for most inspections dark field DF lighting has a. Scattering Differential interference contrast microscopy uses polarized light to produce multiple images that are superimposed and produce interference highlighting differences in the refractive index of different parts of the cell producing a false 3D effect.
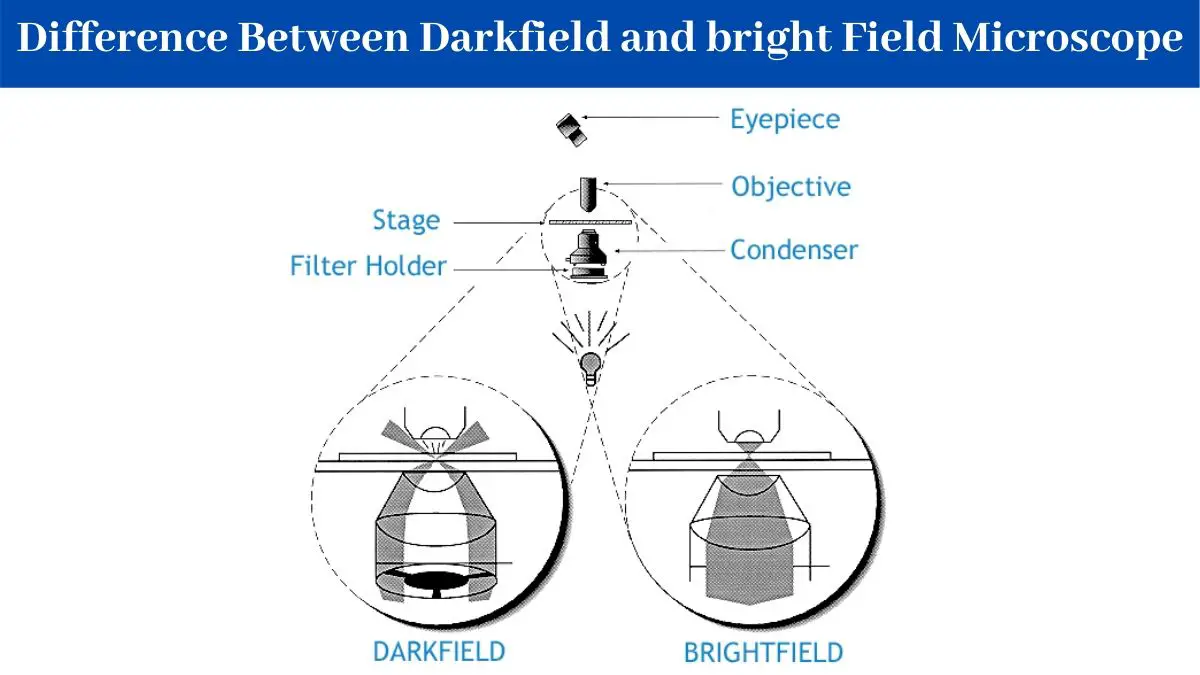
The microbes to be observed must be killed fixed and stained. Microscope Slides 1 by 3 in. Dark field microscopy In dark field microscopy the specimen is lit by a hollow yet focused cone of light that is controlled by the condenser.
Scanning electron microscopy relies on electrons reflecting from the specimen. Dark-field microscopy depends on which characteristic of light. The condenser used in the dark field microscope scatters the light rays if there is any light source.
Dark field microscopy can be achieved by trans-illumination or by epi-illumination. Dark-field microscopy depends on which characteristic of light. The objective lens rests just outside this bright area and this light travels around the lens without actually entering the cone set by the condenser.
The dark field microscope it is a special optical instrument used in certain laboratories. Scattering In dark field microscopy the scattering of light allows objects smaller than the wavelength to be viewed as bright images on a dark field Scattering 6. Conversely dark field lighting involves orienting lights between 0 and 45 degrees off horizontal which is particularly effective when imaging highly reflective surfaces or generating edge effects.
A disadvantage of dark-field microscopy is thatChoose one. A disadvantage of dark-field microscopy is one. The design of the dark field microscope is such that it removes the dispersed light or zeroth order so that only the scattered beams hit the sample.
To view a specimen in dark field an opaque disc is placed underneath the condenser lens so that only light that is scattered by objects on the slide can reach the eye. Darkfield microscopy is a technique that takes advantage of oblique illumination to enhance contrast in specimens that are not imaged well under normal illumination conditions. The characteristic of light that allows magnification by a microscope isChoose one.
It only reveals the same structures as bright-field microscopy. Dark field microscopy is a light microscopy technique that uses oblique incident illumination to image samples. The microbes to be observed must be killed fixed and stained.
In optical microscopes a darkfield condenser lens must be used which directs a cone of light away from the objective lens. Dark-field microscopy describes microscopy methods in both light and electron microscopy which exclude the unscattered beam from the image. Instead of coming up through the specimen the light is reflected by particles on the slide.
Both techniques have advantages and disadvantages. It is one type of light microscope others being bright-field phase-contrast differential interface contrast and fluorescence. Bright-field microscopy relies on light absorption and dark-field microscopy relies on light scattered by the specimen.
Dark-field microscopy depends on which characteristic of light. In a typical method light is shone onto the microscopes sample stage at a steep angle with respect to the sample surface normal. Dark-Field Light Microscope This is a specialized type of bright field light microscope that has several similarities to the Phase-Contrast Microscope.
As a result the field around the specimen is generally dark. Any objects in the specimen will scatter light leading to increased background noise. In this microscopy the specimen is brightly illuminated while the background is dark.
Learning Objectives Generalize the process of dark-field microscopy Key Takeaways Key Points In dark-field microscopy the light reaches the specimen from an angle with the help of an opaque disk. Dark-field microscopy is a technique that can be used for the observation of living unstained cells and microorganisms. Both phase-contrast microscopy and X-ray crystallography produce images based on interference patterns generated by light interacting with the specimen.
This is the result of a modification made to brightfield microscopy. After the direct light has been blocked by an opaque stop in the condenser light passing through the specimen from oblique angles. It only reveals the same structures as bright-field microscopy.
Everything is visible regardless of color usually bright white against a dark background. Dark-field microscopes show a light silhouette of an organism against a dark background. The whole scattering of light depends on the light source.
Dark-field microscope with parfocal 10 40 to 45 and 100 oil immersion objectives 10 oculars dark-field immersion condenser single or double deflecting and a 60- to 65-V high-intensity lamp with variable transformer for regulating light intensity. The introduction of a condenser andor stop below the stage ensures that these light rays will hit the specimen at different angles rather than as a direct light source abovebelow the object. By Alec De Grand - 17 December 2020.
The electrons help in the process of scattering light rays. Since the incident beam is not captured by the objective lens except where it has been scattered by the sample the sample image has a dark background. Coverslip 22 by 22 mm.
A disadvantage of dark-field microscopy is that. A dark field microscope can offer brilliant light images against a dark background of otherwise difficult to view specimensMost standard microscopes come with dark field capabilities or accessories to enable this illumination techniqueThere are many practical applications of dark field especially in the field of marine biology in viewing. A dark-field microscopic observation was carried out to evaluate the light-scattering characteristics of the Au NPs adsorbed on a bacterium as shown in Fig.
The Au NPs-adsorbed bacterium can be clearly observed in Fig. To make a dark field Microscope place a darkfield stop underneath and a condenser lens which produces a hollow cone beam of light that enters the objective only from the specimen Prescott pg 22.

Principle Of Dark Field Microscopy Download Scientific Diagram

0 Comments